What Is the Retina?
The retina is a nerve layer at the back of your eye that senses light and sends images to your brain. An eye is like a camera. The lens in the front of the eye focuses light onto the retina. You can think of the retina as the film that lines the back of a camera.
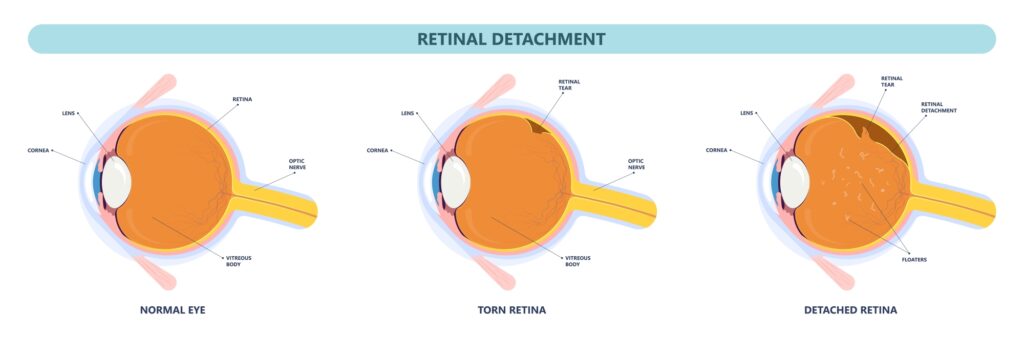
What Is a Retinal Detachment?
A retinal detachment occurs when the retina is pulled away from its normal position. The retina does not work when it is detached. Vision is blurred, like a camera picture would be blurry if the film were loose inside the camera. A retinal detachment is a very serious problem that almost always causes blindness unless it is treated.
What Causes Retinal Detachment?
The vitreous is a clear gel that fills the middle of the eye. As we get older, the vitreous may pull away from its attachment to the retina at the back of the eye. Usually the vitreous separates from the retina without causing problems. But sometimes the vitreous pulls hard enough to tear the retina in one or more places. Fluid may pass through the retinal tear, lifting the retina off the back of the eye, like wallpaper can peel off a wall.
The following conditions increase the chance that you might get a retinal detachment:
- Nearsightedness
- Previous cataract surgery
- Glaucoma
- Severe injury
- Previous retinal detachment in your other eye
- Family history of retinal detachment
- Weak areas in your retina that can be seen by your ophthalmologist or optometrist
What are the Warning Symptoms of a Retinal Detachment?
These early symptoms may indicate the presence of a retinal detachment:
- Flashing lights
- New floaters
- A gray curtain moving across your field of vision
These symptoms do not always mean a retinal detachment is present; however, you should see your ophthalmologist or optometrist as soon as possible.
What Treatment Is Needed?
Most retinal tears need to be treated with laser surgery or cryotherapy (freezing), which seals the retina to the back wall of the eye. These treatments cause little or no discomfort and may be performed in your ophthalmologist’s office. Treatment of a retinal tear usual prevents retinal detachment. Almost all patients with retinal detachment require surgery to put the retina back in its proper position.
What are the Risks?
Any surgery has risks; however, an untreated retinal detachment usually results in permanent severe vision loss or blindness. Most retinal detachment surgery is successful, although a second operation is sometimes needed.
Will Your Vision Improve?
Vision may take many months to improve and in some cases never return fully. Unfortunately, some patients do not recover any vision. The more severe the detachment, the less vision may return. For this reason, it is very important to see your ophthalmologist or optometrist at the first sign of any trouble.

